中国组织工程研究 ›› 2014, Vol. 18 ›› Issue (23): 3660-3663.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.2014.23.009
• 干细胞基础实验 basic experiments of stem cells • 上一篇 下一篇
巴斯德消毒法可否影响血红蛋白理化性质及生物学功能?
李凤娟1,2,冯 杰2,李 燊3,杨成民2,3
- 1天津工业大学环境与化学工程学院,天津市 300384;2天津协和生物科技发展研究所,天津市 300457;3中国医学科学院北京协和医学院输血研究所,四川省成都市 610052
Pasteurization affects the physicochemical properties and biological function of hemoglobin?
Li Feng-juan1,2, Feng Jie2, Li Shen3, Yang Cheng-min2, 3
- 1School of Environmental and Chemical Engineering, Tianjin Polytechnic University, Tianjin 300384, China; 2 Tianjin Union Institute of Biotechnology Development, Tianjin 300457, China; 3Institute of Blood Transfusion, Chinese Academy of Medical Sciences, Chengdu 610052, Sichuan Province, China
摘要:
背景:巴斯德消毒法对白蛋白的病毒灭活条件已很完善,可不要求进行病毒灭活验证,但将其应用于血红蛋白类血液代用品病毒灭活的研究在国内外尚未见有系统报道。
目的:探讨巴斯德消毒法对血红蛋白类血液代用品理化性质及生物学功能的影响。
方法:取适量脐血,经离心、洗血、破膜、添加稳定剂处理后,对照组于55 ℃水浴加热,待血红蛋白溶液温度达到(55±1) ℃开始计时,2 h后加热处理完成;巴氏消毒组于60 ℃水浴加热,待血红蛋白溶液温度达到(60±1) ℃开始计时,10 h后加热处理完成,该过程持续通氮保护。然后置冰浴冷却到 4 ℃以下,低温高速离心,微孔滤膜过滤,得到纯化及病毒灭活的脐血血红蛋白。
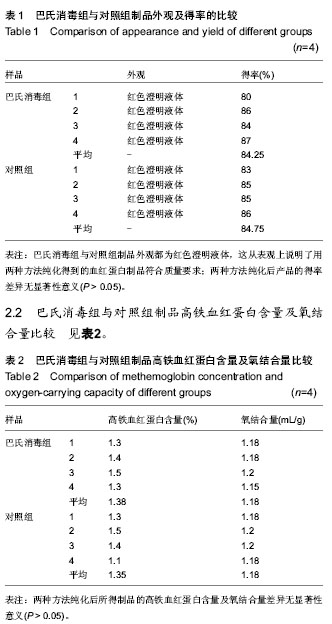
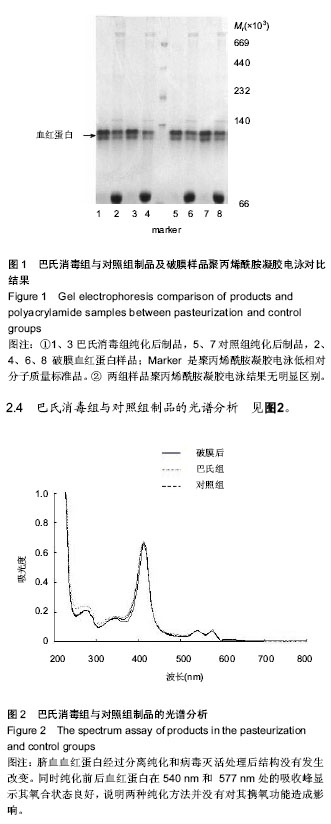
结果与结论:巴氏消毒组与对照组制品外观都为红色澄明液体;在得率、高铁血红蛋白含量、氧结合量方面两组差异无显著性意义;两组的纯度都在98%以上;两种纯化方法并没有对血红蛋白携氧功能造成影响。因此,可以用巴斯德病毒灭活的方法来代替一直在使用的55 ℃,2 h的热敏法纯化方式。这样不仅能保证血红蛋白的理化性质、生物学性质,还能同时达到病毒灭活的目的。
中图分类号:

.jpg)